javascript动画之圆形运动,环绕鼠标运动作小球
时间:2023-12-09JavaScript动画之圆形运动
在JavaScript中,通过使用CSS3的transform属性或canvas绘图API,可以实现圆形运动效果。接下来,我们以transform属性为例进行详细讲解。
示例1:物体沿圆形路径运动
- 首先,需要准备一个容器和一个要运动的物体。将其设置为圆形,如下所示:
<div id="container">
<div id="ball"></div>
</div>
<style>
#container {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 50%;
position: relative;
}
#ball {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 50%;
margin-left: -25px;
}
</style>
- 然后,通过JavaScript代码来设置物体沿圆形路径运动的效果。
var container = document.getElementById('container');
var ball = document.getElementById('ball');
var radius = container.clientWidth / 2 - ball.clientWidth / 2; // 半径
var angle = 0; // 角度
setInterval(function() {
var x = container.clientWidth / 2 + radius * Math.cos(angle);
var y = container.clientHeight / 2 + radius * Math.sin(angle);
ball.style.top = y - ball.clientHeight / 2 + 'px';
ball.style.left = x - ball.clientWidth / 2 + 'px';
angle += 0.01; // 每次增加的角度值,可根据实际情况调整
}, 16); // 每隔16毫秒执行一次
- 最后就可以看到物体沿圆形路径运动了。
示例2:环绕鼠标运动的小球
- 首先,准备一个容器和一个小球。
<div id="container2">
<div id="ball2"></div>
</div>
<style>
#container2 {
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
position: relative;
}
#ball2 {
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-color: orange;
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
margin-top: -25px;
margin-left: -25px;
}
</style>
- 然后,通过JavaScript代码来设置小球环绕鼠标运动的效果。
var container2 = document.getElementById('container2');
var ball2 = document.getElementById('ball2');
container2.addEventListener('mousemove', function(ev) {
var x = ev.clientX - container2.offsetLeft;
var y = ev.clientY - container2.offsetTop;
var left = x - ball2.clientWidth / 2;
var top = y - ball2.clientHeight / 2;
var r = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(container2.clientWidth / 2 - x, 2) + Math.pow(container2.clientHeight / 2 - y, 2)); // 小球到容器中心的距离
var angle = Math.acos((x - container2.clientWidth / 2) / r);
if (y > container2.clientHeight / 2) { // 鼠标在容器下半部分
angle = Math.PI * 2 - angle;
}
ball2.style.left = left + r * Math.cos(angle) + 'px';
ball2.style.top = top + r * Math.sin(angle) + 'px';
});
- 最后,运行代码,可以看到小球环绕鼠标运动的效果。
总结
通过以上两个示例,我们可以发现,实现圆形运动效果的核心代码是根据圆的参数方程计算物体的坐标,实现小球环绕鼠标运动的核心是根据三角函数计算物体的坐标。在实际开发中,可以根据具体场景选择使用哪种方式来实现圆形运动效果。
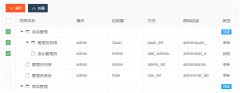 Layui treetable 复选框联动解决方案treetable.js没有checked做联动。于是自己基于treetable开发的一个小功能,希望能和大家一起交流一下。 1. 在当前HTML文档checked监听函数中增加以下代码 //联动 table.on(
Layui treetable 复选框联动解决方案treetable.js没有checked做联动。于是自己基于treetable开发的一个小功能,希望能和大家一起交流一下。 1. 在当前HTML文档checked监听函数中增加以下代码 //联动 table.on(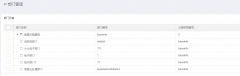 layui扩展的树形表格treetablelayui开发时,遇到要求做成这样的树形表格的需求。这里我们要用到layui的第三方控件treetable,最终实现效果如下图所示: 引入控件: layui.config({ base: '/js/' //直接
layui扩展的树形表格treetablelayui开发时,遇到要求做成这样的树形表格的需求。这里我们要用到layui的第三方控件treetable,最终实现效果如下图所示: 引入控件: layui.config({ base: '/js/' //直接