JS中call apply bind函数手写实现demo
时间:2023-12-09下面是关于“JS中call apply bind函数手写实现demo”的攻略:
理解call、apply、bind函数
在手写这三个函数的过程中,我们必须先清楚地理解这三个函数的作用:
- call函数:调用一个函数,将一个对象作为第一个参数,以及多个参数传入该函数。
- apply函数:调用一个函数,将一个对象作为第一个参数,以及一个参数数组传入该函数。
- bind函数:创建一个新函数,该函数与原始函数具有相同的函数体,但this值被永久地绑定到了bind函数的第一个参数中。
手写call函数
call函数的实现过程如下:
Function.prototype.myCall = function (context) {
// 首先要获取调用call的函数,用this可以获取
const calledFunc = this
// context为传入的需要调用函数的对象
context = context || window
// 从arguments中获取到需要传递的参数
const args = [...arguments].slice(1)
// 将该函数作为传入的对象的方法调用,以改变函数的this指针
context.fn = calledFunc
// 最后把参数传入进去并执行
const result = context.fn(...args)
// 删除对象上的方法
delete context.fn
return result
}
示例:
function sayName() {
console.log(this.name)
}
const person = { name: 'Lucas' }
sayName.myCall(person) // 'Lucas'
手写apply函数
apply函数的实现过程如下:
Function.prototype.myApply = function (context) {
// 首先要获取调用apply的函数,用this可以获取
const calledFunc = this
// context为传入的需要调用函数的对象
context = context || window
// 从arguments中获取到需要传递的参数
const args = arguments[1]
// 将该函数作为传入的对象的方法调用,以改变函数的this指针
context.fn = calledFunc
// 最后把参数传入进去并执行
const result = context.fn(...args)
// 删除对象上的方法
delete context.fn
return result
}
示例:
function sayName(age) {
console.log(`My name is ${this.name}, and I'm ${age} years old`)
}
const person = { name: 'Lucas' }
sayName.myApply(person, [25]) // 'My name is Lucas, and I'm 25 years old'
手写bind函数
bind函数的实现过程如下:
Function.prototype.myBind = function (context) {
// 首先要获取调用bind的函数,用this可以获取
const calledFunc = this
// context为传入的需要调用函数的对象
context = context || window
// 从arguments中获取到需要传递的参数
const args = [...arguments].slice(1)
// 返回一个新的函数,此时该函数的this指向已经绑定到了context上
return function () {
const newArgs = args.concat([...arguments])
return calledFunc.apply(context, newArgs)
}
}
示例:
function sayName(age) {
console.log(`My name is ${this.name}, and I'm ${age} years old`)
}
const person = { name: 'Lucas' }
const sayNameWithPerson = sayName.myBind(person)
sayNameWithPerson(25) // 'My name is Lucas, and I'm 25 years old'
总结
通过手写call、apply、bind这三个函数,可以更深刻地理解它们的作用,并且掌握函数指针和this的相关知识点。在实际编码中,也可以更加灵活地应用这些函数,让代码实现更加简洁高效。
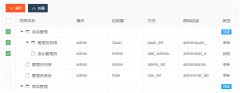 Layui treetable 复选框联动解决方案treetable.js没有checked做联动。于是自己基于treetable开发的一个小功能,希望能和大家一起交流一下。 1. 在当前HTML文档checked监听函数中增加以下代码 //联动 table.on(
Layui treetable 复选框联动解决方案treetable.js没有checked做联动。于是自己基于treetable开发的一个小功能,希望能和大家一起交流一下。 1. 在当前HTML文档checked监听函数中增加以下代码 //联动 table.on(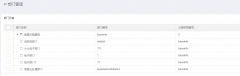 layui扩展的树形表格treetablelayui开发时,遇到要求做成这样的树形表格的需求。这里我们要用到layui的第三方控件treetable,最终实现效果如下图所示: 引入控件: layui.config({ base: '/js/' //直接
layui扩展的树形表格treetablelayui开发时,遇到要求做成这样的树形表格的需求。这里我们要用到layui的第三方控件treetable,最终实现效果如下图所示: 引入控件: layui.config({ base: '/js/' //直接