js学习笔记之class类、super和extends关键词
时间:2023-12-07JS学习笔记之Class类、super和extends关键词攻略
介绍
在ES6之前,JavaScript是一门纯粹的面向对象语言,而没有类的概念,而是采用基于原型的继承方式。在ES6之后,JavaScript引入了Class类、super和extends关键词,使得JavaScript的面向对象变得更加完善。Class语法让JavaScript的对象声明,操作和继承更加直观。
- Class:定义一个包含特定属性和方法的对象模板,通过new实例化或者extends继承使用
- super:super关键字用于调用父类的构造函数,或者调用父类中的方法和属性
- extends:用来继承某个类,可以在一个子类中使用 extends关键字后接父类名,然后在构造函数中调用super方法来调用父类的构造函数
Class类
创建一个类
在JavaScript中创建一个类很简单,只需要使用class关键字就可以定义一个类,然后使用new关键字进行实例化
class Person{
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
greeting(){
console.log(`Hello, my name is ${this.name}, I'm ${this.age} years old.`);
}
}
let person1 = new Person('John', 30);
person1.greeting(); //输出:Hello, my name is John, I'm 30 years old.
类的继承
继承是面向对象编程中的一个重要概念,ES6提供了Class关键字来实现类的继承,也就是子类可以继承父类的属性和方法
class Student extends Person{
constructor(name, age, major){
super(name, age);
this.major = major;
}
introduce(){
console.log(`My major is ${this.major}.`);
}
}
let student1 = new Student('Lucy', 20, 'Math');
student1.greeting(); //输出:Hello, my name is Lucy, I'm 20 years old.
student1.introduce(); //输出:My major is Math.
super
super关键字是一种引用父类方法的方式,它可以用来调用父类方法或者构造函数。在子类的构造函数中,如果要使用父类的构造函数,就需要使用super方法。 当我们需要继承父类的方法时,也可以通过super关键字调用父类的方法,并且可以带上相关的参数
class Animal{
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
}
run(){
console.log(`${this.name} is running.`);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
constructor(name, breed){
super(name);
this.breed = breed;
}
run(){
super.run();
console.log(`A ${this.breed} dog is running.`);
}
}
let dog1 = new Dog('Mike', 'Husky');
dog1.run(); //输出:Mike is running. A Husky dog is running.
在子类的run()方法中调用父类的run()方法,打印出“Mike is running.”。之后,又打印出了“`A Husky dog is running.”
extends
extends关键字用于类之间的继承,在一个子类中使用extends关键字继承父类的属性和方法。利用继承,可以使用父类进行代码共享,并且可以更容易地扩展类的功能,同时也可以更好地维护代码
class Animal{
constructor(name){
this.name = name;
}
run(){
console.log(`${this.name} is running.`);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
constructor(name, breed){
super(name);
this.breed = breed;
}
shout(){
console.log(`A ${this.breed} dog is barking.`);
}
}
let dog1 = new Dog('Mike', 'Husky');
dog1.run(); //输出:Mike is running.
dog1.shout(); //输出:A Husky dog is barking.
在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个Animal类来创建一个动物对象和一个Dog类来创建一个狗对象。通过extend关键字,Dog类可以继承自Animal类,并且扩展了一个新的方法shout()。
结论
在JavaScript中Class类、super和extends关键词被广泛使用,使得JavaScript的面向对象编程变得更加直观。使用Class类可以方便的创建实例化对象,使用继承可以共享代码,并且更容易地维护代码。super关键字则能够方便地调用父类的方法或构造函数,从而避免了重复性的代码。
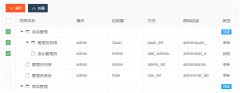 Layui treetable 复选框联动解决方案treetable.js没有checked做联动。于是自己基于treetable开发的一个小功能,希望能和大家一起交流一下。 1. 在当前HTML文档checked监听函数中增加以下代码 //联动 table.on(
Layui treetable 复选框联动解决方案treetable.js没有checked做联动。于是自己基于treetable开发的一个小功能,希望能和大家一起交流一下。 1. 在当前HTML文档checked监听函数中增加以下代码 //联动 table.on(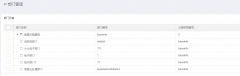 layui扩展的树形表格treetablelayui开发时,遇到要求做成这样的树形表格的需求。这里我们要用到layui的第三方控件treetable,最终实现效果如下图所示: 引入控件: layui.config({ base: '/js/' //直接
layui扩展的树形表格treetablelayui开发时,遇到要求做成这样的树形表格的需求。这里我们要用到layui的第三方控件treetable,最终实现效果如下图所示: 引入控件: layui.config({ base: '/js/' //直接